Enumerating Atom Substitutions
Problem
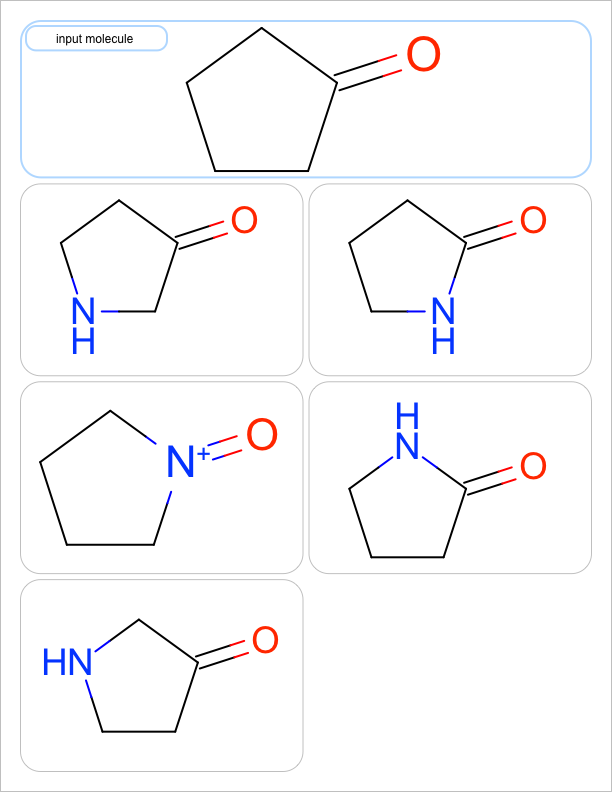
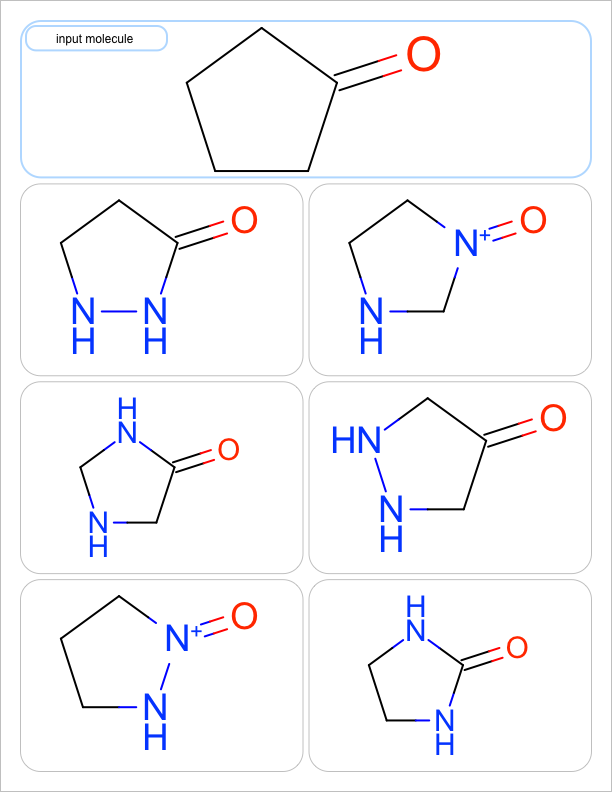
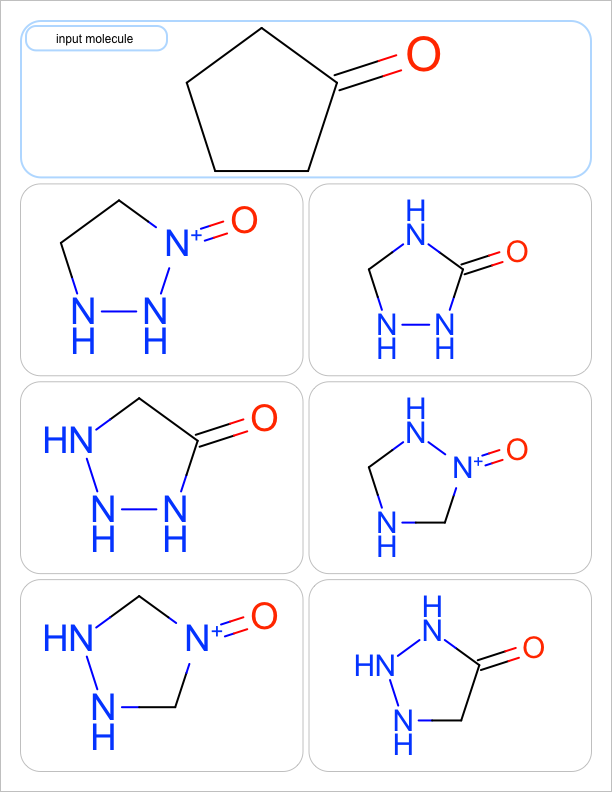
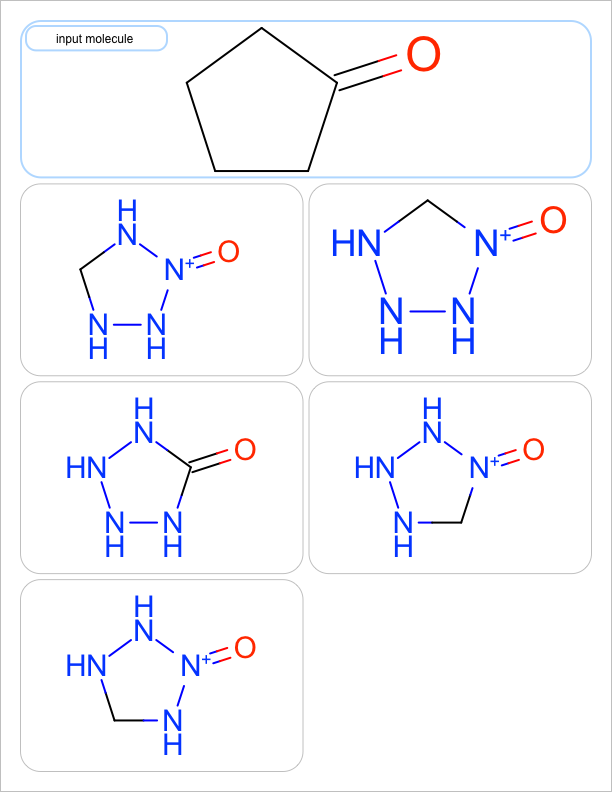
You want to enumerate all possible carbon to nitrogen atom substitutions in a molecule. See examples in Table 1
one substitution |
two substitutions |
three substitutions |
four substitutions |
|
|
|
|
Ingredients
|
Difficulty Level

Solution
The EnumerateSubstitutions function below generates all possible combinations of the given atom indices in the range of [minsubs - maxsubs].
1def EnumerateSubstitutions(mol, minsubs, maxsubs, atompred=oechem.OEIsCarbon()):
2
3 oechem.OESuppressHydrogens(mol)
4 mol.Sweep()
5 atomindices = [atom.GetIdx() for atom in mol.GetAtoms(atompred)]
6
7 submols = []
8
9 for n in range(minsubs, maxsubs + 1):
10 for atomcomb in combinations(atomindices, n):
11 smol = oechem.OEGraphMol(mol)
12 if PerformSubstitution(smol, atomcomb):
13 submols.append(oechem.OEGraphMol(smol))
14
15 return submols
The PerformSubstitution function carries out the carbon atom to nitrogen atom substitutions defined by the given atom combination. After setting the atomic number, the implicit hydrogen count and the charge of the altered atoms are corrected in order to generate chemically correct molecules.
1def PerformSubstitution(mol, atomcomb):
2
3 for aidx in atomcomb:
4 atom = mol.GetAtom(oechem.OEHasAtomIdx(aidx))
5 if atom is None:
6 return False
7 atom.SetAtomicNum(oechem.OEElemNo_N)
8
9 # correct hydrogen count and charge
10 valence = 3
11 hcount, charge = 0, 0
12
13 if valence > atom.GetExplicitValence():
14 hcount = valence - atom.GetExplicitValence()
15 charge = 0
16 elif valence < atom.GetExplicitValence():
17 hcount = 0
18 charge = atom.GetExplicitValence() - valence
19
20 atom.SetImplicitHCount(hcount)
21 atom.SetFormalCharge(charge)
22
23 return True
After enumerating all possible atom substitutions, the molecules are written to the output stream by calling the WriteUniqueMolecules function. In order to avoid outputting duplicate molecules, the OEMolToSmiles function is used to generate canonical isomeric SMILES. The OEMolToSmiles function generates the same SMILES string for isomorphic molecules i.e. molecules that only differ by atom ordering. See example of graph isomorphic molecules in Table 2.
1def WriteUniqueMolecules(mols, ofs):
2 uniqsmiles = set()
3 for mol in mols:
4 smi = oechem.OEMolToSmiles(mol)
5 if smi not in uniqsmiles:
6 uniqsmiles.add(smi)
7 oechem.OEWriteMolecule(ofs, mol)
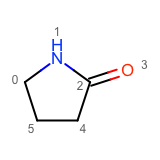
|
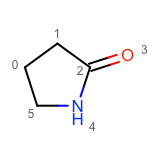
|
Download code
Usage:
prompt > python3 enumsubstitutions.py -in .ism -out .ism -minsubs 1 -maxsubs 2
C1CC(=O)CC1
Running the above commands will generate the following output:
C1CNCC1=O
C1CC(=O)NC1
C1CC[N+](=O)C1
C1CNNC1=O
C1C[N+](=O)CN1
C1C(=O)NCN1
C1C(=O)CNN1
C1CN[N+](=O)C1
C1CNC(=O)N1
See the first two columns of the Table 1 that depict the one and two atom substitutions of the input molecule C1CC(=O)CC1.
Discussion
The EnumerateSubstitutions function takes an atom predicate that determines which atoms are being substituted. By default, it only allows substitution of carbon atoms. OEChem TK has a diverse selection of built-in atom predicates and also allows the creation of user-defined ones. This provide a flexible and convenient way to determine the set of atoms to be substituted. For example when using the OEIsHeavy predicate, the enumeration of any two substitutions will result in the following extra three molecules for the cyclopentanone input structure:
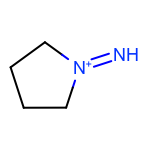
|
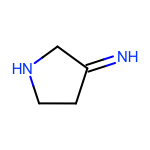
|
|
See also in Python documentation
See also in OEChem TK manual
Theory
Predicates Functors chapter
API
OEAtomBase class
OEAtomBase.SetImplicitHCount method
OEIsCarbon and OEIsHeavy predicates
OEMolBase.Sweep method
OEMolToSmiles function