Extracting the Smallest Binding Unit from a Design Unit (January 31, 2024)
What you will learn: How to lower compute cost by reducing a design unit to the smallest binding unit needed for your calculations.
Estimated read time: 2 minutes.
With the Subset Design Unit to Smallest Binding Unit floe, you can modify Spruce-prepared design units (DUs) to retain only the smallest essential unit for binding. This process involves removing other protein chains, making it suitable for specific calculations, such as molecular dynamics-based approaches, and helping to reduce overall costs.
For instance, when working with dimeric structures in a DU, if the binding site is in chain A based on the binding site residue location, the floe can efficiently exclude the chain B, streamlining the simulation setup for better cost-effectiveness.

A floe for streamlining a simulation setup.
This floe also retains the solvent component based on a certain distance (default 5 Å) to other components (with options to select).
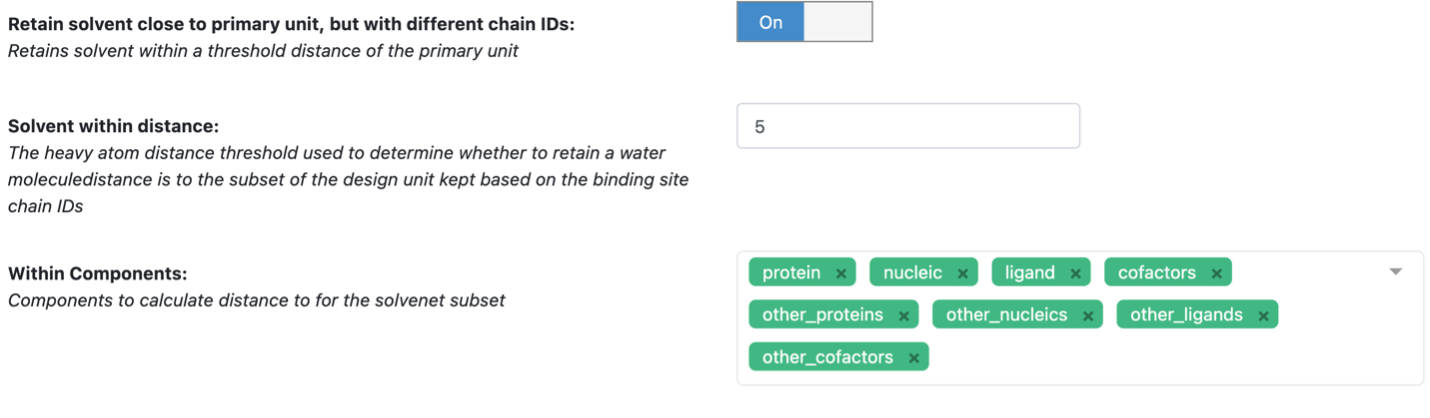
Options available.
As an example, consider structures like the human Thr160-phospho CDK2/cyclin A complex with the inhibitor (PDB ID 1H1Q). This floe enables you to selectively remove protein chains that are not directly involved in binding to the inhibitor.
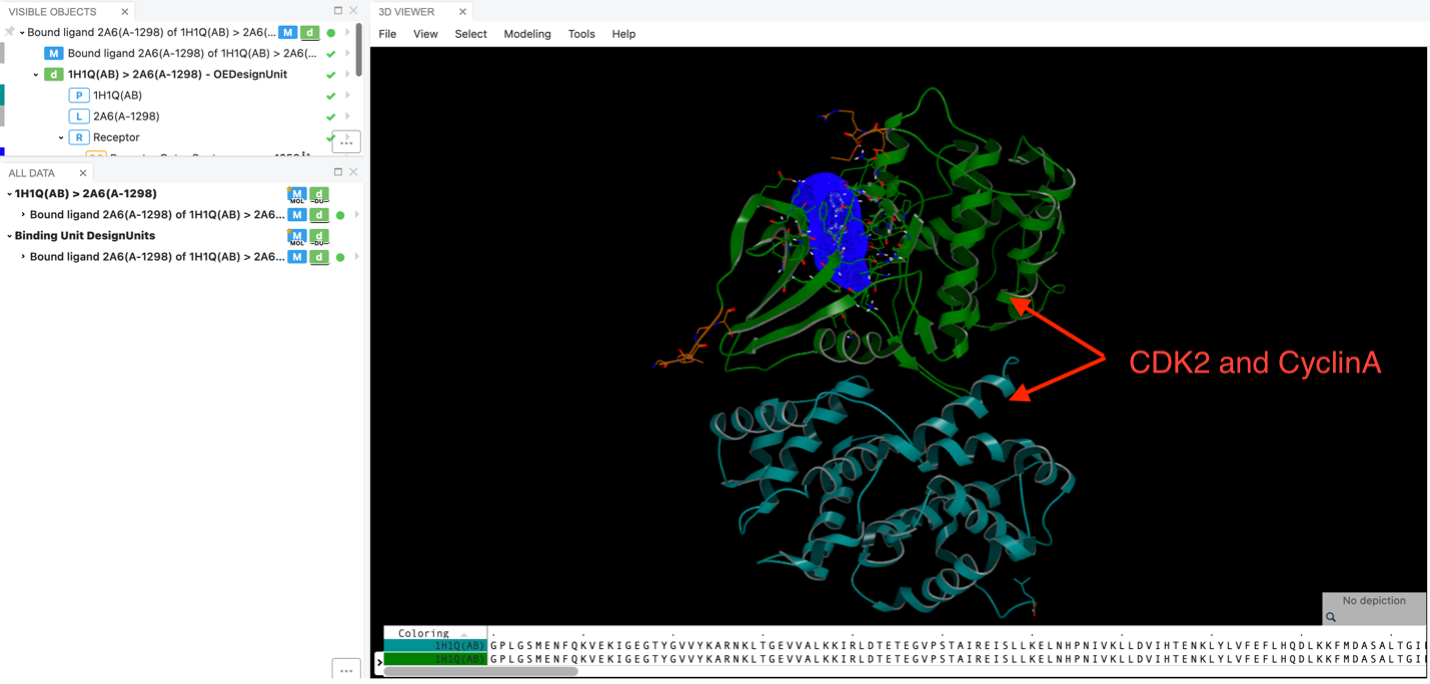
Three-D analysis with two chains.
Specifically, in the Spruce prepared DU for 1H1Q, both CDK2 and cyclin A are present. Since the inhibitor binds to CDK2, using this floe allows you to eliminate the nonbinding chain, cyclin A.
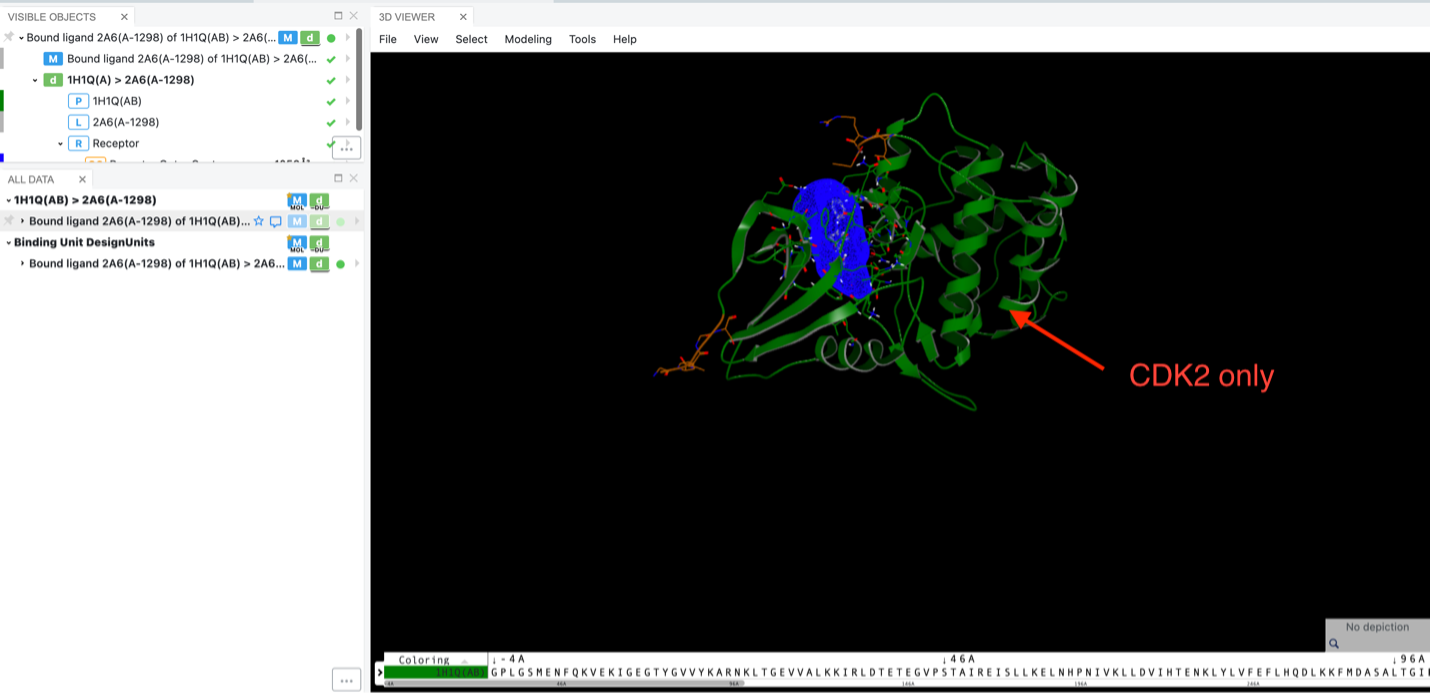
Reduction to one chain.
Please note that while this floe offers a useful solution for operating on protein chains according to your specific needs, it is not always recommended to reduce the size to a monomer. Kindly use your scientific discretion.