OEToolkits 2025.2
Release Highlights 2025.2
Shape: Features Extension
New functionalities have been added to improve Shape TK and ROCS handling of queries beyond those derived from molecules. Major new features include using queries consisting only of color atoms or Gaussians (Figure 1), and the ability to search a database of grids as well as molecules. The ability to work with non-molecular queries has also been enhanced by introducing a new algorithm to generate Gaussians from a grid that can better capture sparse grids (Figure 2).
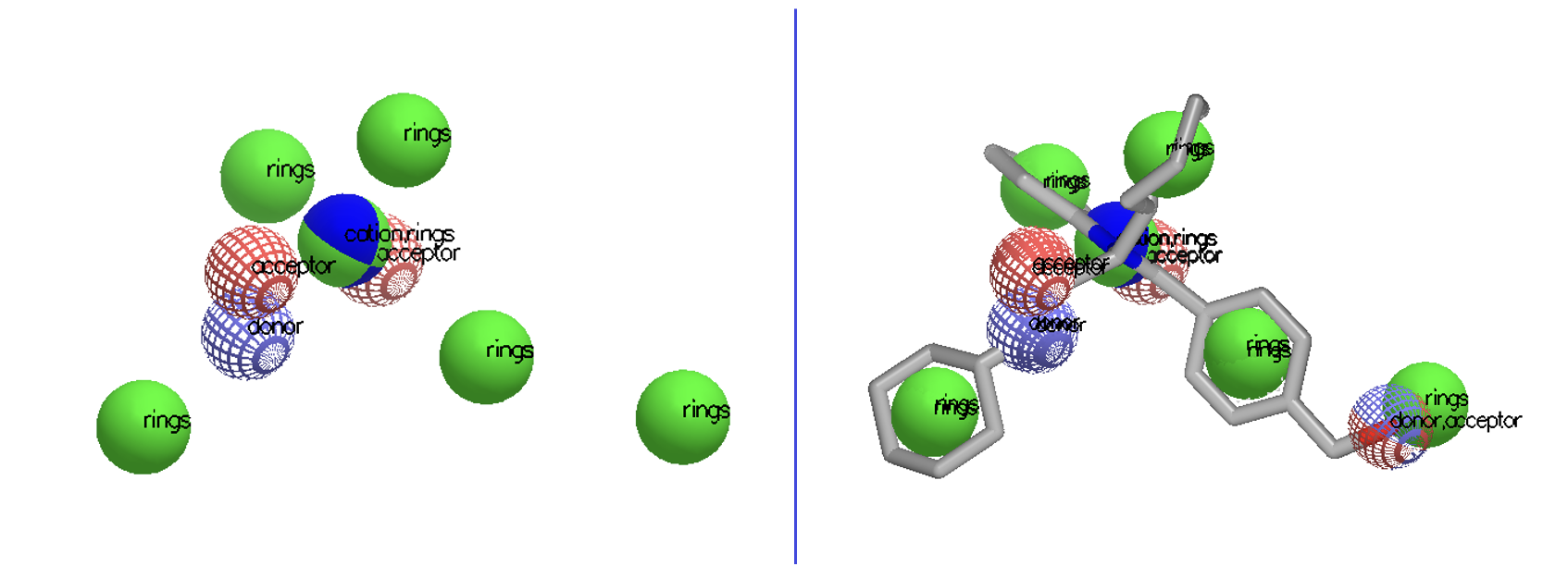
Figure 1. A color-only query consisting only of color Gaussians (left). The overlay of a molecule on that color-only query (right).
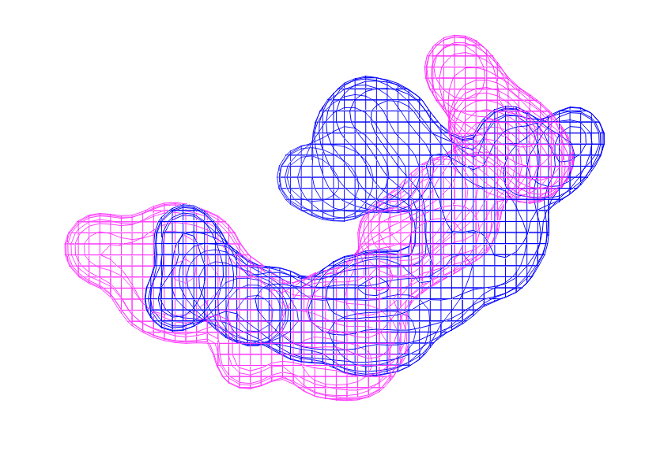
Figure 2. The overlay of a grid on another grid as query.
Saiph TK: New Toolkit for ETL
This release introduces Saiph TK, a toolkit for extracting, transforming, and loading (ETL) files, bringing the existing Orion ETL functionality for file conversion into the toolkits, providing greater accessibility and improved performance.
Major functionality in the Saiph TK includes conversion of various molecule file formats, including SMILES and CXSMILES, SD, Spruce TK design unit files, and Shape TK query files, into a set of records. Saiph TK also provides functionality to interconvert CSV files and records, and to create a Pandas dataframe directly from any supported format, enabling smooth integration of molecule objects into machine learning in Python.
OEChem TK and Spruce TK: Improvements to CIF File Format Support
The Worldwide Protein Data Bank (wwPDB) has officially deprecated the legacy PDB file format in favor of mmCIF. The format has recently been expanded to include residue topology information, and the RCSB has worked to ensure that all deposited structures include these new mmCIF-specific categories. In alignment with wwPDB and RCSB recommendations, we now advise using the mmCIF format for all macromolecular structures.
To support the transition, the CIF file reader in OEChem has been improved particularly in regard to reading the mmCIF file format variant. New APIs have been added that allow parsing and modification of the mmCIF metadata. Improvements to CIF file writing has also been made to be more correct when header data is missing or has been manually altered.
The Spruce filter now leverages mmCIF header data to refine structure perception during standardization prior to preparation. Additionally, support has been added for reading structure factor CIF files into grids, replacing MTZ files for electron density maps.
Supported Platforms
Package
Versions
Linux
Windows
macOS
Python
3.10 - 3.13
RHEL8/9, Ubuntu22/22-ARM/24
Win10/11
13, 14, 15
C++
RHEL8/9, Ubuntu22/22-ARM/24
Win10/11 (VS2022)
13, 14, 15
Java
8, 11, 21
RHEL8/9, Ubuntu22/22-ARM/24
Win10/11
13, 14, 15
C#
Win10/11 (VS2022)
General Notices
Support for Python 3.13 has been added for all supported platforms.
Support for Python 3.10 will be dropped in the Spring 2026 release, and Python 3.11 will be dropped in the fall of 2026.
Support for Python 3.14 will be added in the Spring 2026 release.
Support for macOS 26 will be added in the Spring 2026 release, and support for macOS 13 will be dropped.
Support for Windows 10 will be dropped in the Spring 2026 release.