SMARTS Pattern Matching
SMARTS Syntax
SMARTS is a line notation developed by Daylight Chemical Information Systems for compactly representing molecular substructure queries. The SMARTS language can be considered an extension or generalization of Daylight’s SMILES notation for representing discrete molecules.
A SMARTS syntax overview can be found at the documentation of SMARTS on the Daylight Chemical Information Systems site
Atom Primitives
Symbol |
Description |
Argument? |
Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
|
non-aromatic (aliphatic) atom |
no |
(no default) |
|
aromatic atom |
no |
(no default) |
|
degree (explicit connections) |
yes |
(no default) |
|
total hydrogen count |
optional |
exactly one |
|
implicit hydrogen count |
optional |
exactly one |
|
ring bond count [1] |
optional |
any ring atom |
|
ring bond count [2] |
optional |
any ring atom |
|
smallest ring size |
optional |
any ring atom |
|
valence (total bond order) |
yes |
(no default) |
|
connectivity (total connections) |
yes |
(no default) |
|
atomic number |
yes |
(no default) |
|
positive charge |
optional |
+1 cation (++ is +2, etc) |
|
negative charge |
optional |
-1 anion (– is -2, etc) |
|
atomic hybridization [3] |
yes |
(no default) |
|
anticlockwise local chirality |
no |
|
|
clockwise local chirality |
no |
|
|
chirality class |
optional |
anticlockwise |
|
atomic mass no |
Table footnote:
[1]
The semantics of the ring count primitive, R, differs slightly between
Daylight SMARTS and OpenEye SMARTS.
In Daylight semantics, R<n> means that an atom is in n rings of the
chosen SSSR.
As the choice of SSSR is non-deterministic, this interpretation can cause an
arbitrary set of atoms to match depending upon input order.
For example, in the symmetric molecule, cubane, four of the eight atoms will
appear in two SSSR rings, and half of the atoms appear in three, but the choice is
made almost randomly. Rather than attempt to reproduce these weak
semantics, OpenEye strengthens the definition of R<n> to mean the
number of ring bonds to an atom, which is graph invariant and therefore
independent of a molecule’s input order. Notice, that the interpretation of
[R] and [R0], i.e. ring membership, remains the same.
Similarly, Daylight [R1] is approximately equal to OpenEye [R2],
and Daylight [R2] is approximately equivalent to OpenEye [R3].
[2]
Note that [x] was implemented by Daylight v4.9 and OEChem TK 1.5, and is
exactly synonymous to OEChem TK’s [R].
[3]
The atomic hybridization primitive, ^, is an OpenEye* extension that
is not available in Daylight SMARTS, but can be implemented using
recursive SMARTS.
Bond Primitives
Syntax |
Description |
|---|---|
default |
single or aromatic |
|
single bond (not aromatic) |
|
double bond (not aromatic) |
|
triple bond |
|
any bond (wildcard) |
|
aromatic bond |
|
ring bond |
|
directional single ‘up’ bond |
|
directional single ‘down’ bond |
|
directional ‘up’ or unspecified |
|
directional ‘down’ or unspecified |
Logical Operators
Syntax |
Description |
|---|---|
|
not |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Examples
SMARTS: |
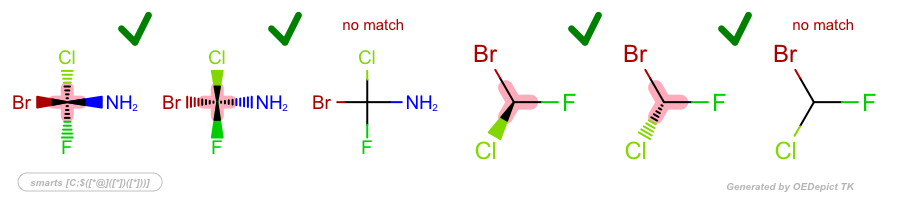
|
SMARTS: |
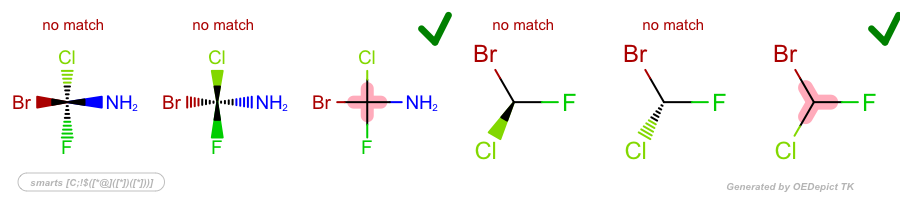
|