Run BROOD
vBROOD runs the BROOD command line application using a query. It can run BROOD on multiple processors, provide access to the command line options, display the output of the command line in a log window, and display the best fragments found as the run progresses.
Load a Query
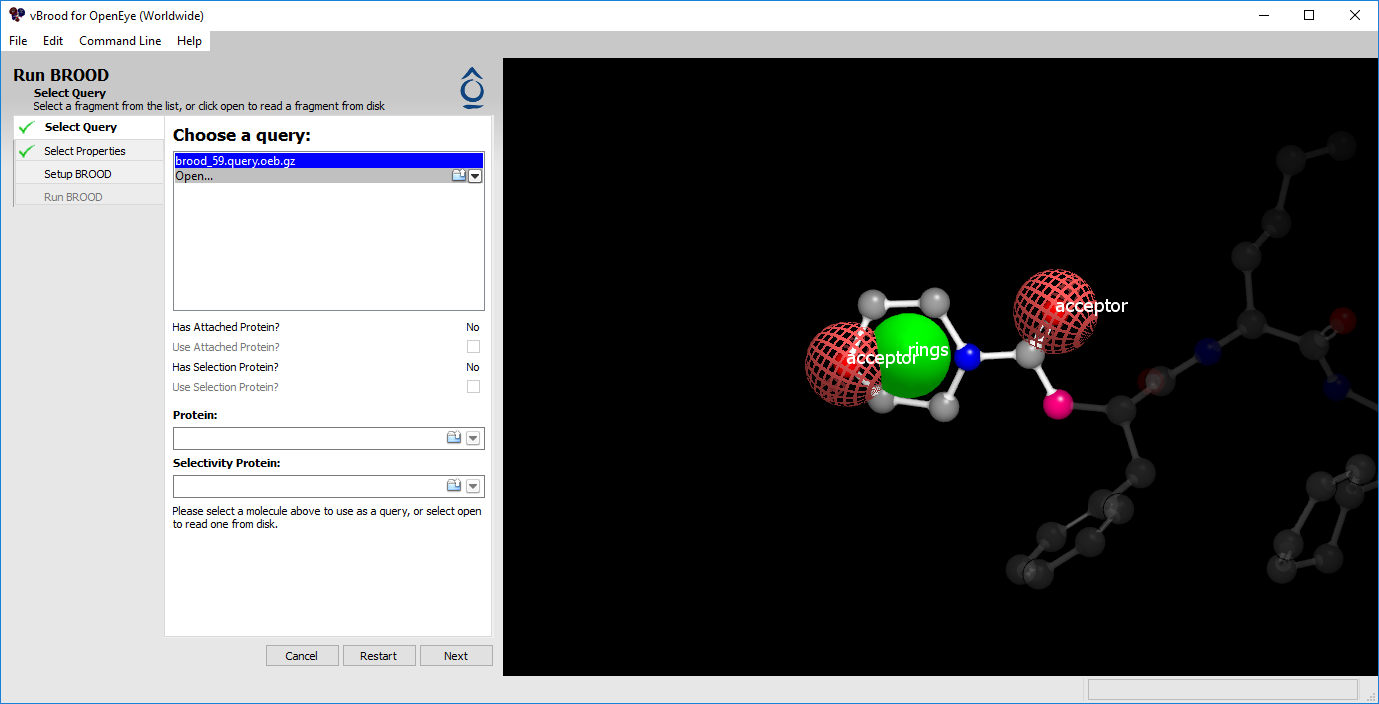
Figure 1. Loading a query.
The first step to running BROOD is to load or select a query.
Previously built queries appear in the query list.
Queries can be loaded by clicking the Open option.
If the query does not have an associated protein, clicking on the Open icon in the Protein text box will allow you to add one.
After a query is selected, it is displayed in the 3D window. Once it is loaded, clicking “Next” will take you to Select a Filter.
Select a Filter
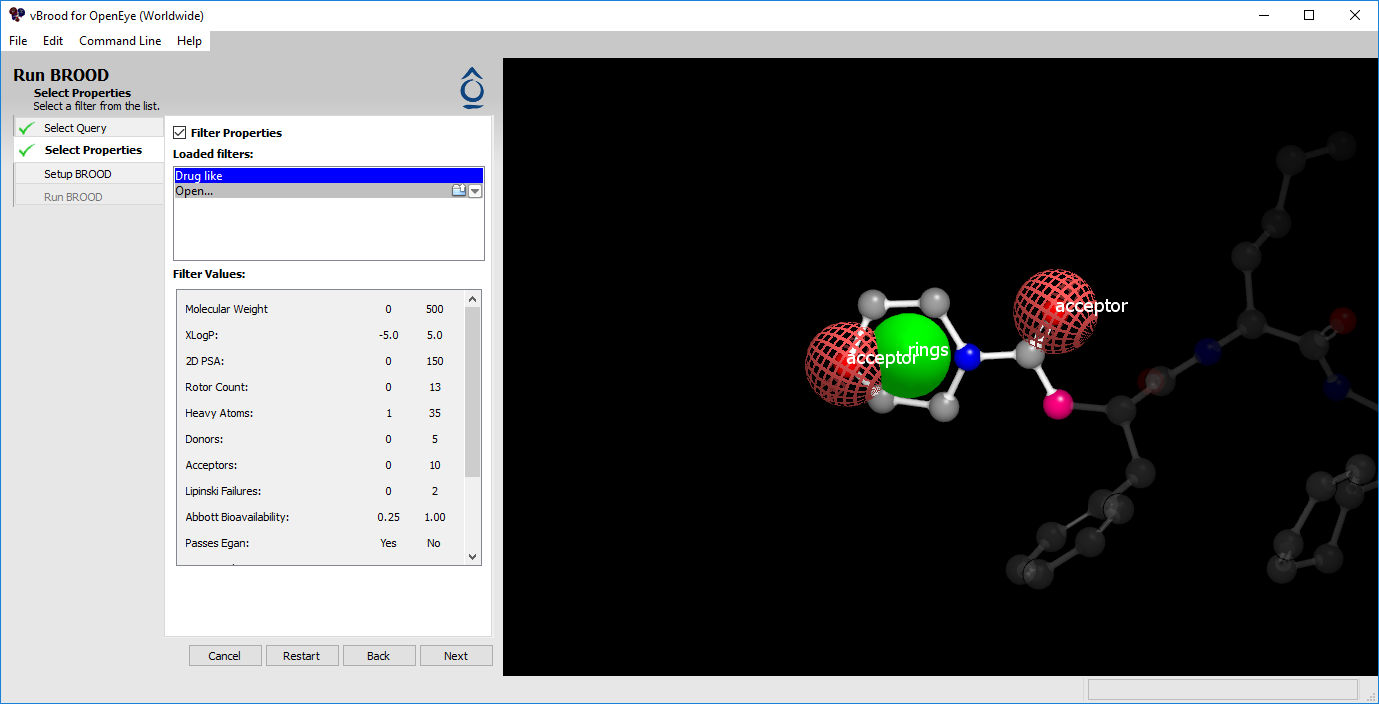
Figure 2. Choosing a filter.
A filter can limit the BROOD search and can shorten the run time. vBROOD provides a built-in drug-like filter; you can also build additional filters. To use a filter, select one from the list or open a previously saved filter.
To open a previously saved filter:
Click the Open item in the list. This brings up a dialog that can be used to select a filter.
Select a filter file and click Open. This adds and selects a new entry in the list.
Alternatively, you can select a filter from the Recents menu. Selecting a filter will display its given properties in the Filter Values box below the filter list. When you are satisfied, click “Next” to continue to Set up BROOD.
Set Up BROOD
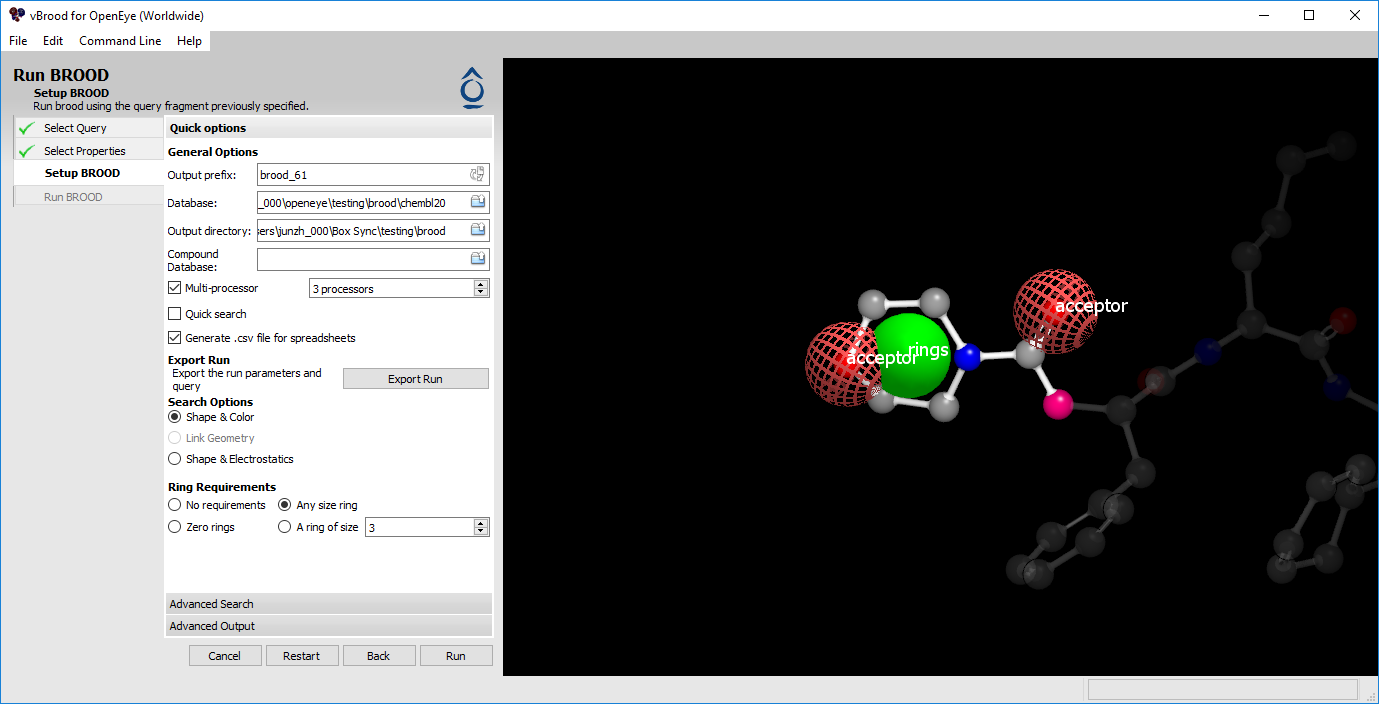
Figure 3. Options for running BROOD.
The next step in running BROOD is choosing the run parameters. Most options correspond directly to a command line option. Hovering over most elements in the interface provides a brief description of the option as well as the command line flag it represents.
The multiprocessor options, found in the Quick Options section, are particularly useful. These options allow you to run multiple BROOD instances using OpenMPI on the same machine as vBROOD. This allows additional processors to be used if they are available.
When all options are set, click “Run” to start the BROOD run and advance to the Run BROOD page.
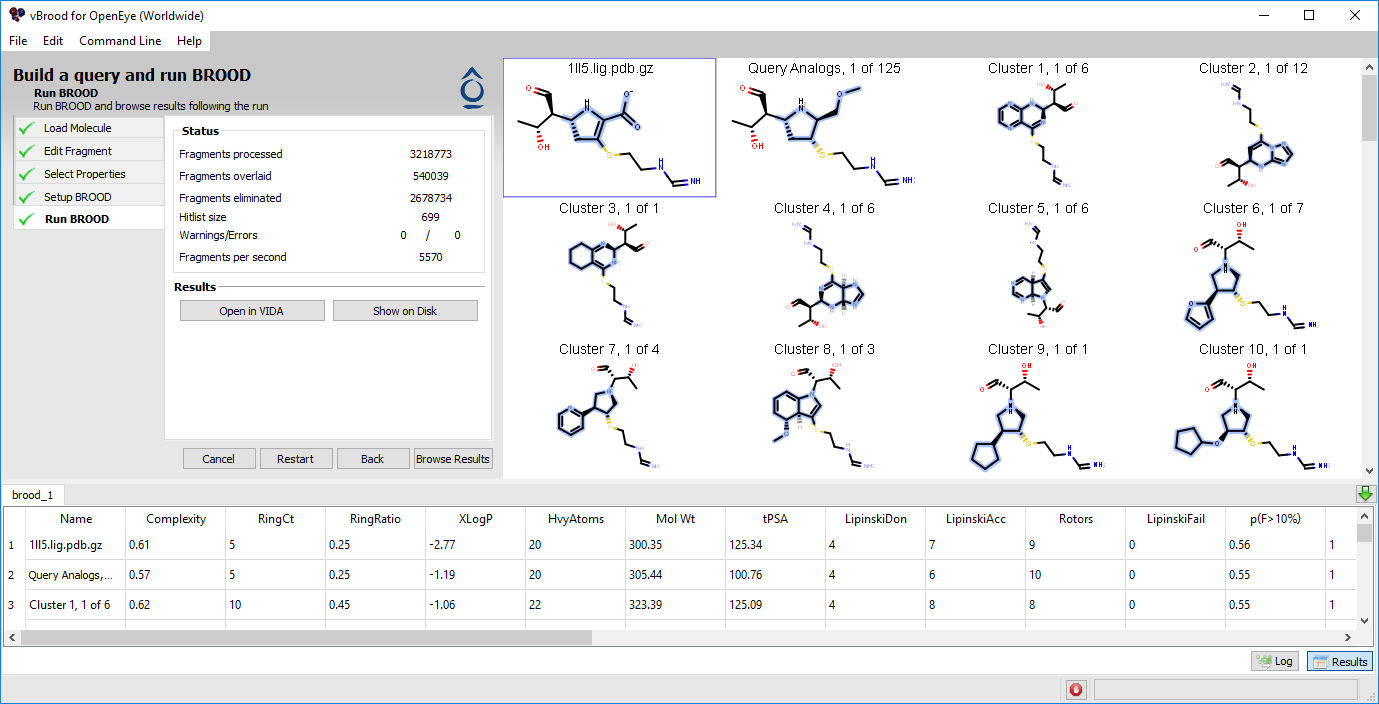
Run BROOD
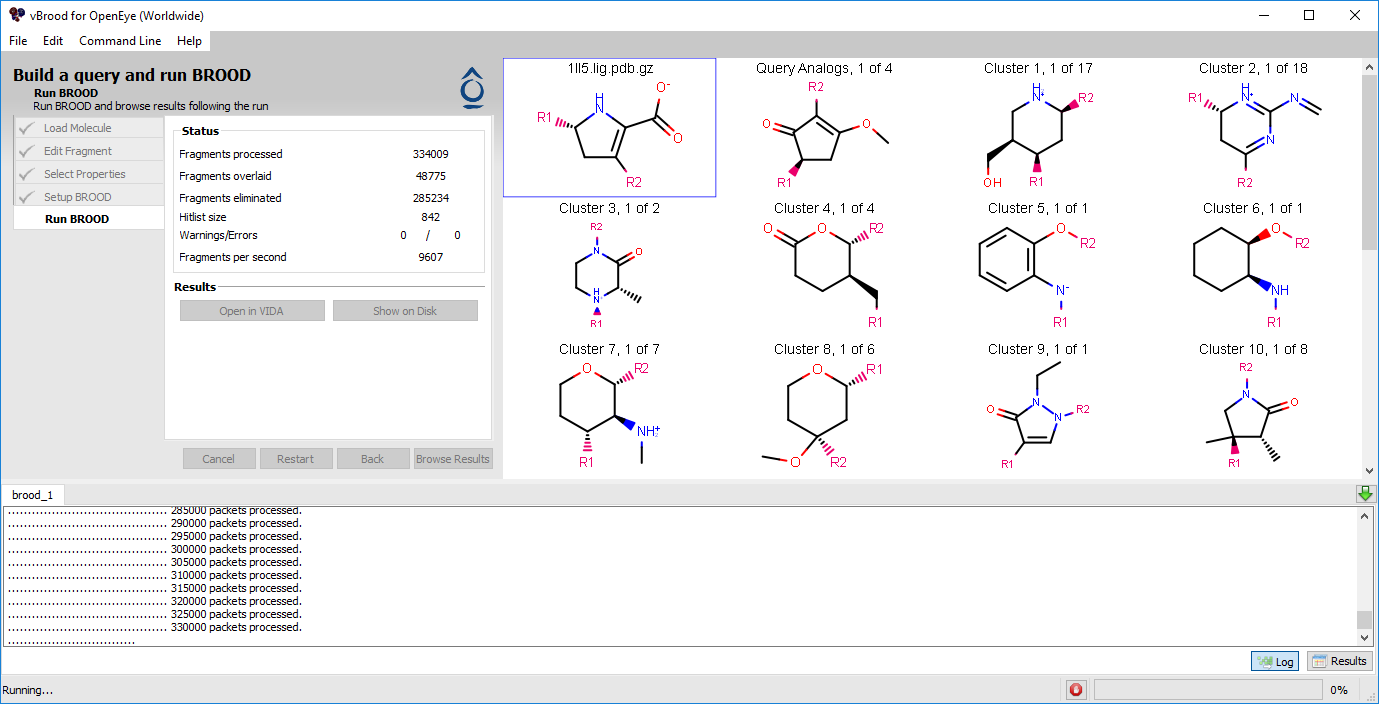
|
|
A run in progress |
A completed run |
Figure 4. A comparison of in-progress and completed BROOD runs.
The screen will then switch to display a 2D hit list, the Output window, and the Status window. This display will dynamically update as the run progresses.
The Hit list shows the current cluster heads from the database.
The Status window on the left shows information about how many fragments have been processed, how many were actually scored against the query, and how many were eliminated.
The Output window at the bottom displays the output of the BROOD run as if it were run from the command line. You can toggle between this output log and a spreadsheet of the top results by using by using the “Log” and “Results” buttons on the bottom right.
At the bottom right of the vBROOD window is a progress bar and a “Stop” icon for aborting the run.
As the run progresses, the top results are displayed in the 2D hit list and the results spreadsheet continues to update. Both the spreadsheet and the 2D hit list provide scrollbars for browsing the hit list. Clicking on a 2D depiction highlights the same row in the spreadsheet and vice versa.
After a run completes, the buttons “Open in VIDA” and “Show on Disk” will be displayed and enabled. Clicking on “Open in VIDA” opens VIDA with the BROOD Results Viewer tool loaded (see Viewing Results in VIDA). Clicking “Show on Disk” opens a window displaying the directory containing the results of the run. If the run did not complete successfully, BROOD displays a dialog box, and the Output window at the bottom shows the Log view. Scanning the log may provide an indication of the problem.
Click “Browse Results” to bring up the list of all runs for the current session. See View Results for more information.