Drawing a Molecule Surface
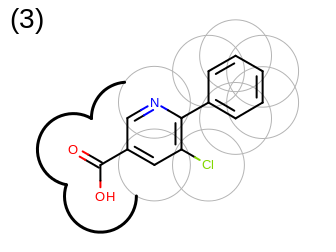
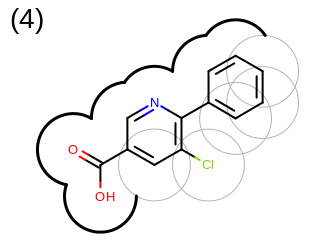
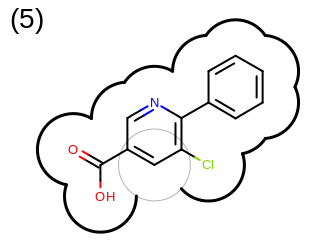
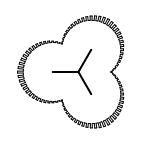
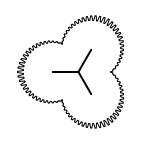
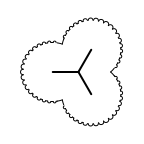
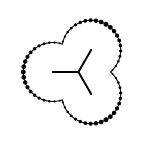
The 2D representation of the molecule surface is calculated by first drawing circles around each atom of the molecule and then identifying the external arc segments that define a continuous surface around the molecule. This process is illustrated in the table Table: Calculation of the 2D representation of a molecule surface
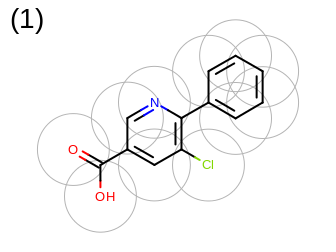
|

|
|
|
|
|
The following Listing 1 example shows how to
the display a molecule surface.
After creating an image object and preparing the molecule for 2D
depiction, an arc drawing functor is added to each atom of the
molecule by using the OESetSurfaceArcFxn
function.
The surface then can be drawn by calling the
OEDraw2DSurface function that calculates the
arc segments that form a continuous curve around the molecule.
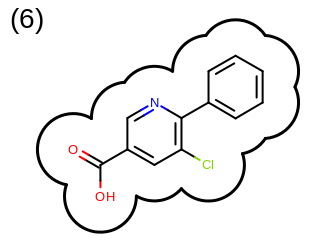
The image created by Listing 1 is shown in
Figure: Example of surface drawing.
Listing 1: Example of surface drawing
opts = oedepict.OE2DMolDisplayOptions(imagewidth, imageheight, oedepict.OEScale_AutoScale)
opts.SetTitleLocation(oedepict.OETitleLocation_Hidden)
opts.SetScale(oegrapheme.OEGetMoleculeSurfaceScale(mol, opts))
arcfxn = oegrapheme.OEEyelashArcFxn(oedepict.OEPen(oechem.OEGrey, oechem.OEGrey))
for atom in mol.GetAtoms():
oegrapheme.OESetSurfaceArcFxn(mol, atom, arcfxn)
disp = oedepict.OE2DMolDisplay(mol, opts)
oegrapheme.OEDraw2DSurface(disp)
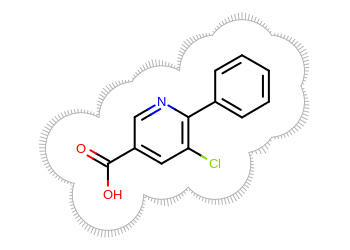
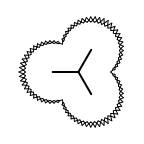
Example of surface drawing
The Listing 1 example uses the
OESurfaceArcStyle_Eyelash style to draw the
molecule surface.
The following table lists all surface drawing styles that are
available in Grapheme TK.
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
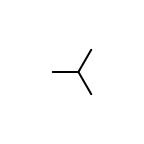
|
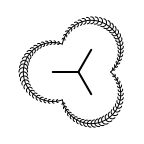
|
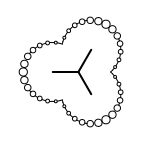
|
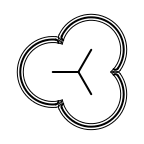
|
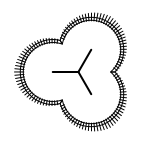
|
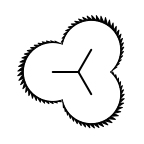
|
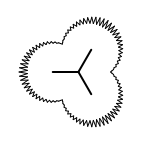
|

|
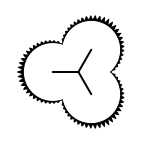
|
|
||
User-defined surface drawing functors can be implemented by deriving
from the OESurfaceArcFxnBase abstract base class.
In the Listing 2 example,
a user defined arc drawing functor is implemented that colors the
eyelash arcs according to the atom they belong to.
The image created by Listing 2 is shown in
Figure: Example of user-defined surface drawing.
Listing 2: Example of user-defined surface drawing
class AtomColorArcFxn(oegrapheme.OESurfaceArcFxnBase):
def __call__(self, image, arc):
adisp = arc.GetAtomDisplay()
if adisp is None or not adisp.IsVisible():
return False
color = adisp.GetLabelFont().GetColor()
pen = oedepict.OEPen(color, color, oedepict.OEFill_Off, 1.0)
center = arc.GetCenter()
radius = arc.GetRadius()
bgnAngle = arc.GetBgnAngle()
endAngle = arc.GetEndAngle()
oegrapheme.OEDrawEyelashSurfaceArc(image, center, bgnAngle, endAngle, radius, pen)
return True
def Draw2DSurface(image, mol):
oedepict.OEPrepareDepiction(mol)
opts = oedepict.OE2DMolDisplayOptions(image.GetWidth(), image.GetHeight(),
oedepict.OEScale_AutoScale)
opts.SetTitleLocation(oedepict.OETitleLocation_Hidden)
opts.SetScale(oegrapheme.OEGetMoleculeSurfaceScale(mol, opts))
arcfxn = AtomColorArcFxn()
for atom in mol.GetAtoms():
oegrapheme.OESetSurfaceArcFxn(mol, atom, arcfxn)
disp = oedepict.OE2DMolDisplay(mol, opts)
oegrapheme.OEDraw2DSurface(disp)
oedepict.OERenderMolecule(image, disp)
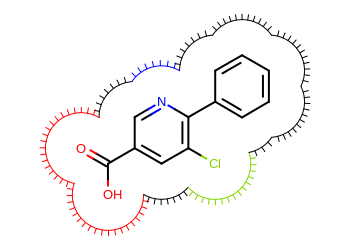
Example of user-defined surface drawing
The Listing 3 example shows
how to project atom properties, such as partial charges into the molecule
surface.
The image created by Listing 3 is shown in
Figure: Example of depicting atom properties.
Listing 3: Example of depicting atom properties on the molecule surface
class AtomPartialChargeArcFxn(oegrapheme.OESurfaceArcFxnBase):
def __init__(self, colorg):
oegrapheme.OESurfaceArcFxnBase.__init__(self)
self.colorg = colorg
def __call__(self, image, arc):
adisp = arc.GetAtomDisplay()
if adisp is None or not adisp.IsVisible():
return False
atom = adisp.GetAtom()
if atom is None:
return False
charge = atom.GetPartialCharge()
if charge == 0.0:
return True
color = self.colorg.GetColorAt(charge)
pen = oedepict.OEPen()
pen.SetForeColor(color)
pen.SetLineWidth(2.0)
center = arc.GetCenter()
radius = arc.GetRadius()
bAngle = arc.GetBgnAngle()
eAngle = arc.GetEndAngle()
edgeAngle = 5.0
dir = oegrapheme.OEPatternDirection_Outside
patternAngle = 10.0
oegrapheme.OEDrawBrickRoadSurfaceArc(image, center, bAngle, eAngle, radius, pen,
edgeAngle, dir, patternAngle)
return True
def CreateCopy(self):
return AtomPartialChargeArcFxn(self.colorg).__disown__()
def Draw2DSurfacePartialCharge(image, mol):
oedepict.OEPrepareDepiction(mol)
oechem.OEMMFFAtomTypes(mol)
oechem.OEMMFF94PartialCharges(mol)
opts = oedepict.OE2DMolDisplayOptions(image.GetWidth(), image.GetHeight(),
oedepict.OEScale_AutoScale)
opts.SetTitleLocation(oedepict.OETitleLocation_Hidden)
opts.SetScale(oegrapheme.OEGetMoleculeSurfaceScale(mol, opts))
coloranion = oechem.OEColorStop(-1.0, oechem.OEColor(oechem.OEDarkRed))
colorcation = oechem.OEColorStop(+1.0, oechem.OEColor(oechem.OEDarkBlue))
colorg = oechem.OELinearColorGradient(coloranion, colorcation)
colorg.AddStop(oechem.OEColorStop(0.0, oechem.OEColor(oechem.OEWhite)))
arcfxn = AtomPartialChargeArcFxn(colorg)
for atom in mol.GetAtoms():
oegrapheme.OESetSurfaceArcFxn(mol, atom, arcfxn)
disp = oedepict.OE2DMolDisplay(mol, opts)
oegrapheme.OEDraw2DSurface(disp)
oedepict.OERenderMolecule(image, disp)
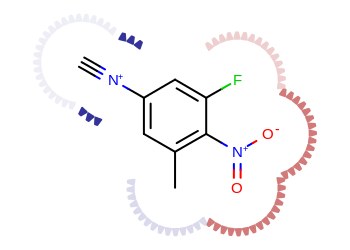
Example of depicting atom properties
See also
OELinearColorGradient class in the OEDepict TK manual
It is also possible to draw multiple 2D surfaces arc-by-arc.
In the Listing 4 example below the
arcs returned by the OEGet2DSurfaceArcs function
for the given atom display and radius are directly rendered below
the molecule diagram.
In this case it is important to call the OEGetMoleculeSurfaceScale
function with the largest radius scale of the 2D surfaces drawn.
This reduces the scaling of the molecule in order to able to fit the
molecule diagram and all of the arcs of the 2D surfaces into the image.
The image created by Listing 4 is shown in
Figure: Example of drawing multiple 2D surfaces.
Listing 4: Example of drawing multiple 2D surfaces
def Draw2DSurface(disp, atompred, radius, color):
penA = oedepict.OEPen(color, color, oedepict.OEFill_Off, 2.0)
arcfxnA = oegrapheme.OEDefaultArcFxn(penA)
penB = oedepict.OEPen(oechem.OELightGrey, oechem.OELightGrey, oedepict.OEFill_Off, 2.0,
oedepict.OEStipple_ShortDash)
arcfxnB = oegrapheme.OEDefaultArcFxn(penB)
layer = disp.GetLayer(oedepict.OELayerPosition_Below)
for adisp in disp.GetAtomDisplays():
for arc in oegrapheme.OEGet2DSurfaceArcs(disp, adisp, radius):
if atompred(adisp.GetAtom()):
arcfxnA(layer, arc)
else:
arcfxnB(layer, arc)
def Draw2DSurfaces(image, mol):
oedepict.OEPrepareDepiction(mol)
opts = oedepict.OE2DMolDisplayOptions(image.GetWidth(), image.GetHeight(),
oedepict.OEScale_AutoScale)
opts.SetTitleLocation(oedepict.OETitleLocation_Hidden)
opts.SetScale(oegrapheme.OEGetMoleculeSurfaceScale(mol, opts, 1.50))
disp = oedepict.OE2DMolDisplay(mol, opts)
Draw2DSurface(disp, oechem.OEHasAtomicNum(oechem.OEElemNo_C), 1.00, oechem.OEBlack)
Draw2DSurface(disp, oechem.OEHasAtomicNum(oechem.OEElemNo_N), 1.25, oechem.OEDarkBlue)
Draw2DSurface(disp, oechem.OEHasAtomicNum(oechem.OEElemNo_O), 1.50, oechem.OEDarkRed)
oedepict.OERenderMolecule(image, disp)
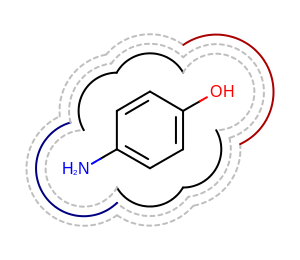
Example of drawing multiple 2D surfaces
See also
OESurfaceArcScale namespace
The last Listing 5 example shows how to
draw a 2D surface with various radii.
It draws two surfaces one with a minimum radius scale and one with various radius
depending on the covalent radius of the atoms.
The OEGetMoleculeSurfaceScale function has to be called
in this example too with the largest radius scale in order to able to fit the molecule diagram
and all of the arcs of the 2D surfaces into the image.
The image created by Listing 5 is shown in
Figure: Example of drawing 2D surface with various radii.
Listing 5: Example of drawing 2D surface with various radii
def DrawSurfaces(image, mol):
oechem.OEAssignCovalentRadii(mol)
minradius = oechem.OEGetCovalentRadius(oechem.OEElemNo_H)
radiusScales = oechem.OEDoubleVector(mol.GetMaxAtomIdx(), 0.0)
maxrscale = float("-inf")
for atom in mol.GetAtoms():
rscale = (atom.GetRadius() - minradius) + oegrapheme.OESurfaceArcScale_Minimum
radiusScales[atom.GetIdx()] = rscale
maxrscale = max(maxrscale, rscale)
opts = oedepict.OE2DMolDisplayOptions(image.GetWidth(), image.GetHeight(),
oedepict.OEScale_AutoScale)
opts.SetTitleLocation(oedepict.OETitleLocation_Hidden)
opts.SetScale(oegrapheme.OEGetMoleculeSurfaceScale(mol, opts, maxrscale))
disp = oedepict.OE2DMolDisplay(mol, opts)
layer = disp.GetLayer(oedepict.OELayerPosition_Below)
penA = oedepict.OEPen(oechem.OELightGrey, oechem.OELightGrey, oedepict.OEFill_Off, 2.0,
oedepict.OEStipple_ShortDash)
arcfxnA = oegrapheme.OEDefaultArcFxn(penA)
for arc in oegrapheme.OEGet2DSurfaceArcs(disp, oegrapheme.OESurfaceArcScale_Minimum):
arcfxnA(layer, arc)
penB = oedepict.OEPen(oechem.OEGrey, oechem.OEGrey, oedepict.OEFill_Off, 2.0)
arcfxnB = oegrapheme.OEDefaultArcFxn(penB)
for arc in oegrapheme.OEGet2DSurfaceArcs(disp, radiusScales):
arcfxnB(layer, arc)
oedepict.OERenderMolecule(image, disp)
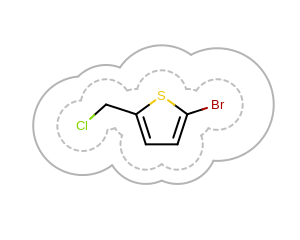
Example of drawing 2D surface with various radii
See also
OEGetCovalentRadius function in the OEChem TK manual