Pocket Ranking by Ligandability Score
OpenEye Ligandability Score Model
How was the model trained?
The OpenEye pocket ligandability score model is trained on a nonredundant dataset consisting of 1477 protein–ligand complex structures. The nonredundant dataset was prepared by curating high-quality structures (with HT Iridium scores) and then using SiteHopper similarity to remove redundancy at the pocket level. The model was trained by featurization of surface points using 13 descriptors computed using OpenEye Toolkits.
Point features:
Curvature
Potential
Exposed atoms count
Exposed atoms density
Atomic partial charges
Exposed aliphatic atoms density
Exposed aromatic atoms density
Exposed H-acceptor density
Exposed H-donor density
Exposed carbon atoms density
Exposed nitrogen atoms density
Exposed oxygen atoms density
The trained model predicts ligandability of individual surface points based on the above descriptors. The predicted ligandability of individual surface point ranges from 0.0 to 1.0 (most ligandable surface point).
How was the model validated?
The OpenEye pocket ligandability score model was validated against a nonoverlapping validation set consisting of 370 nonredundant protein–ligand structures. Nonredundancy among the validation set and nonoverlap between the validation set and the training set was ensured by SiteHopper similarity between the pockets.
The ligandability score for a pocket is computed as the sum of the square of predicted ligandability of individual surface points lining the pocket.
Ranking of the Cryptic Pockets by the Trained Model
The following ligandability scores and related values will be reported for each pocket in the Pocket Receptors dataset generated by Probe Occupancy Analysis, Dynamic Probe Analysis, Combined Probe Binding Site Analysis, and Exposon Analysis.
- Pocket Ligandability Score
The total ligandability score of a pocket is computed as the sum of the square of predicted ligandability of individual surface points lining the pocket. This score can range from 0 to +inf.
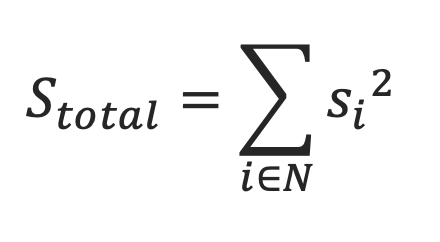
- Normalized Ligandability Score
This is the Pocket Ligandability Score normalized by the total number of surface points lining the pocket. The normalization is done to avoid bias toward pockets with a larger number of surface points. This normalized pocket ligandability score is used for ranking the pockets and selection of the most “ligandable” cluster medoid as the representative structure. The normalized score ranges from 0.0 to 1.0.
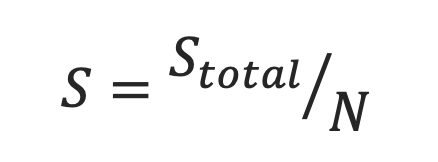
- Ligandability Significance Score
The significance score for the Normalized Ligandability Score is computed as the Bayes factor that ranges from 0.0 to +inf. The Bayes factor is computed from a null distribution of predicted ligandability scores of negative control surface patches and those predicted for known ligand-binding pockets in the above-mentioned validation set consisting of 370 protein–ligand structures. The negative control patches were generated by selecting random protein surface patches not bound to any ligands. The significance score (Bayes factor) measures the likelihood of a predicted pocket to be a ligandable pocket versus the likelihood of it being a non-ligandable site. A pocket with a Ligandability Significance Score of 3.2 or greater (i.e., a Normalized Ligandability Score value of 0.27 or greater) implies strong evidence in favor of a pocket being a ligandable site.
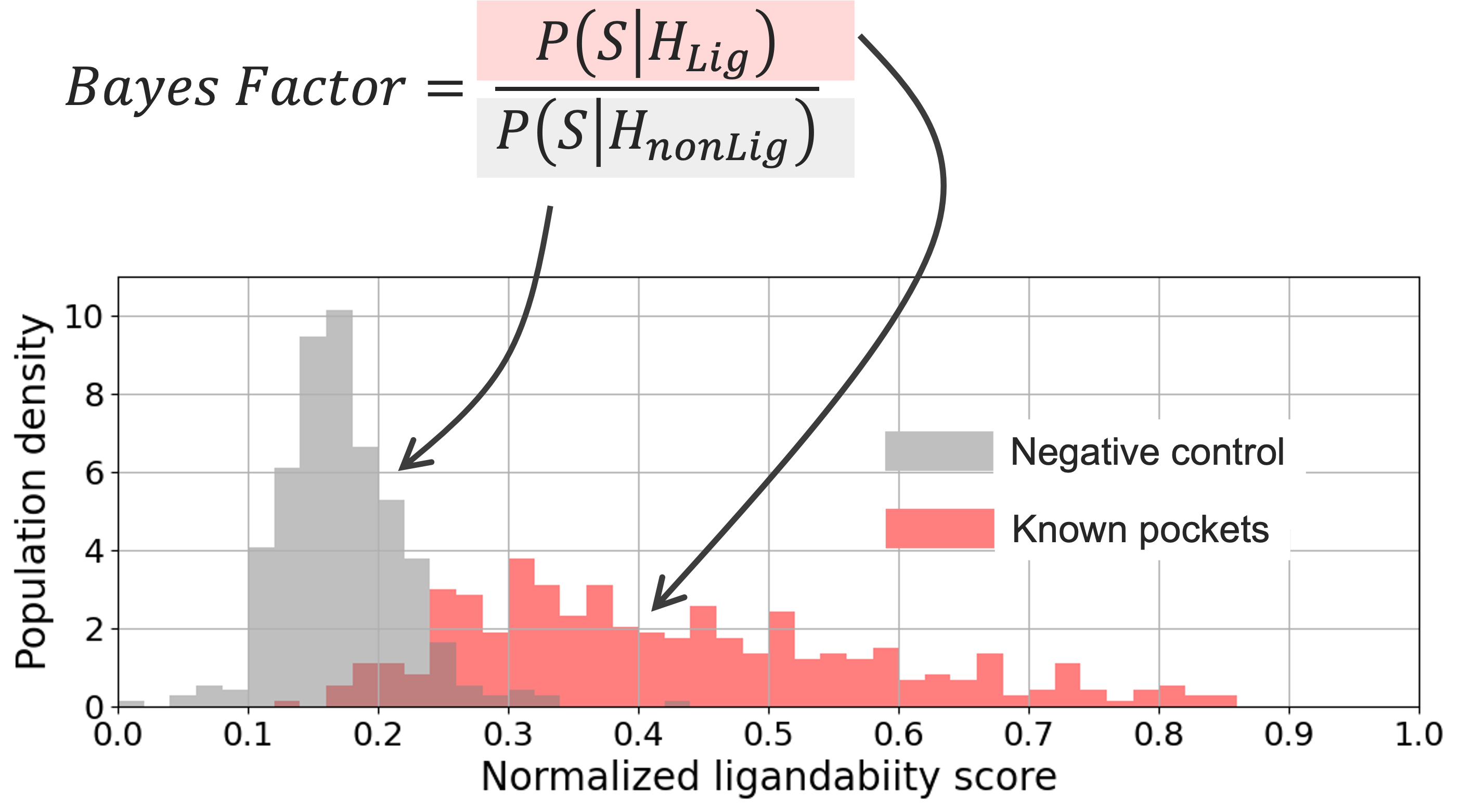
Figure 1. Distribution of predicted ligandability scores for the validation data.
- Ligandability Score per Receptor Volume
This is the total Pocket Ligandability Score normalized by receptor volume; its value can range from 0.0 to +inf. A higher score implies a larger number of ligandable surface points for a given receptor volume. This can be used in conjunction with the Normalized Ligandability Score to select potentially ligandable pockets.
When is the ligandability score model and pocket ranking likely to underperform?
Like every model, our ligandability score model has certain limitations. This model will score pockets binding to unconventional ligands such as peptide/pepetidomimetics, covalent binders, macrocycles.
Such unconventional ligand binding sites might get categorized as unligandable (i.e., normalized ligandability score value less than 0.27) by our scoring model.