Release Notes, Version 2025.3.1
Small Molecule Discovery Suite Highlights
Structural Biology Floes
The new Structural Biology Floes are used to refine Cryogenic Electron Microscopy (cryo-EM) results to protein conformer ensembles. Cryo-EM captures information about the biomolecules’ native conformational ensemble. The floes in this package leverage weighted ensemble molecular dynamics (WEMD) to explore the full protein conformer space defined by the cryo-EM density maps, or mean maps and eigenmaps when available. Even low-resolution maps guide exploration via global shape, enabling the generation of diverse conformers consistent with experimental evidence.
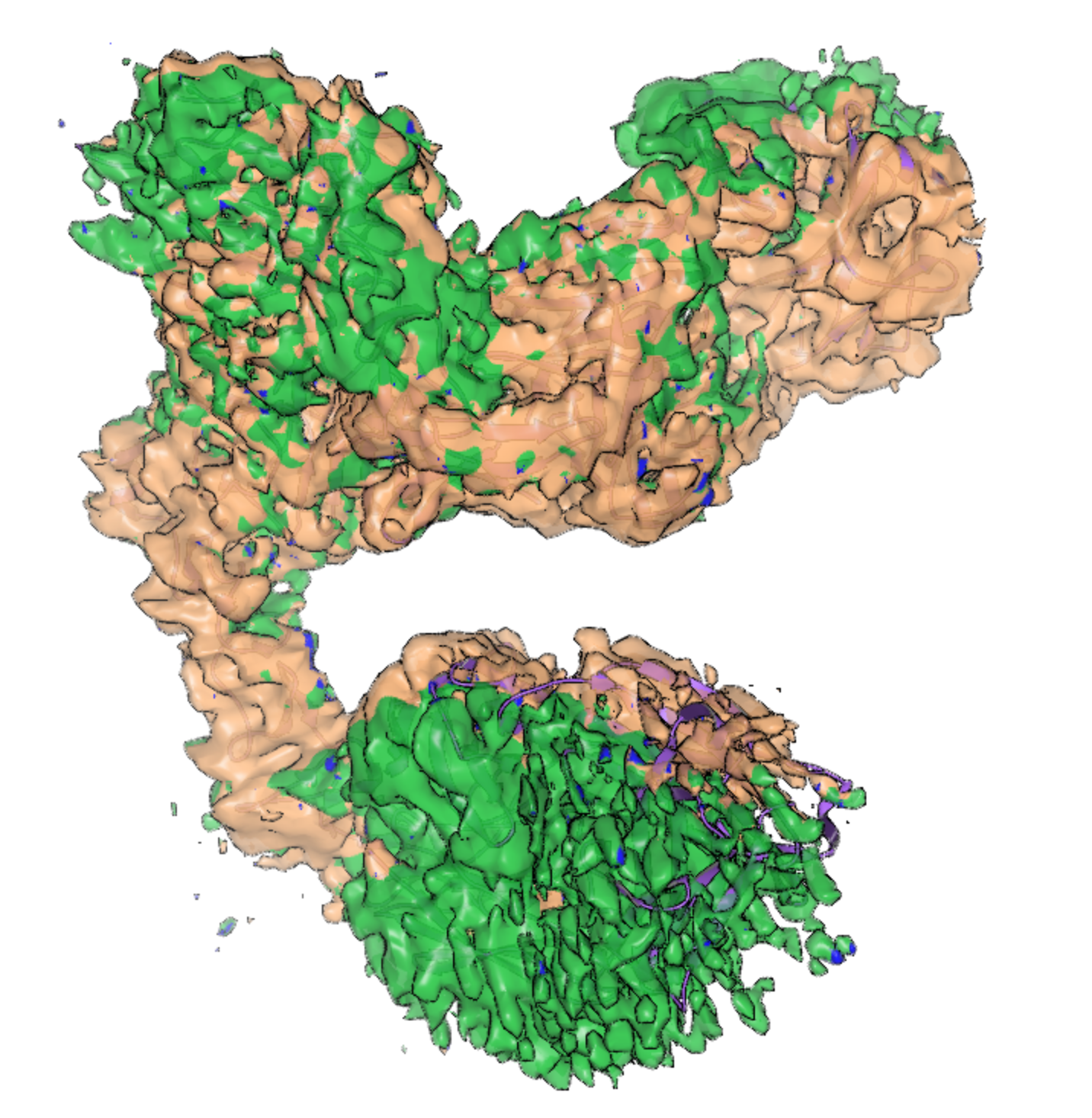
Figure 1. A sample initial protein structure (purple) with cryo-EM density maps, which are used for input in the simulation. The mean map is in blue, and the two heterogeneous maps are in tan and green.
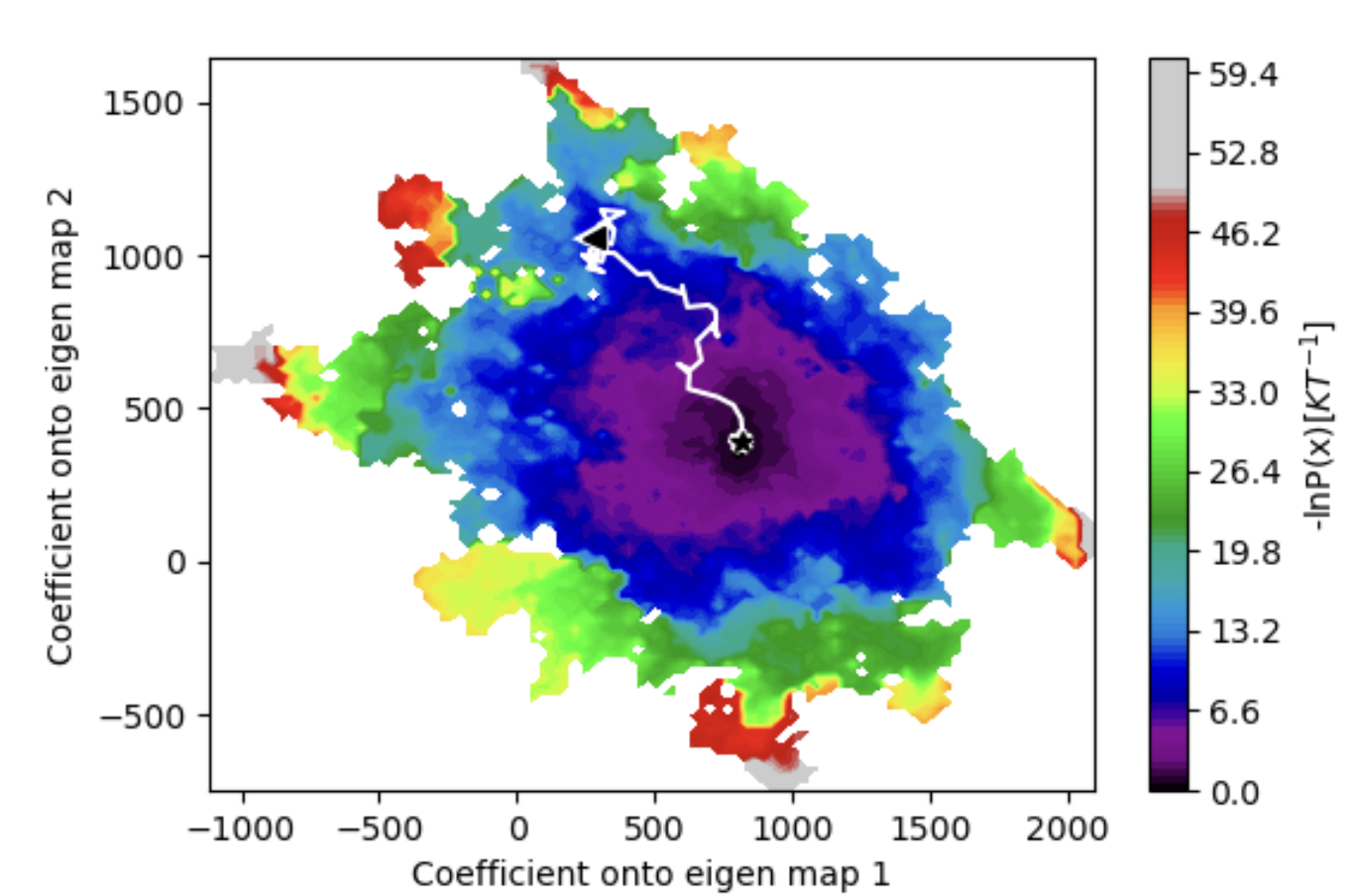
Figure 2. The energy landscape after running weighted ensemble molecular dynamics based on two provided eigenmaps. The metastable state was chosen and an example trajectory is shown for the transition from the starting state to that conformer.
Simulations can be analyzed to identify the best conformers which fit into any provided cryo-EM density maps, even those not used to drive the original WEMD simulation. The resulting energy landscapes can be used to identify metastable states and the transition trajectory between them.
These floes are an affordable way to sample large protein motions, such as secondary structure reorientations or domain motions, potentially requiring only a few WEMD iterations. Each additional density map will be screened against the same simulation to find the best fitting structures; up to dozens of maps can be used simultaneously with minimal added cost.
Output from these floes are all-atom protein conformers which are suitable as input for other calculations, including cryptic pocket detection or SiteHopper.
ML Model Building Floes
ML Build: Graph Convolution Model on Pregenerated Features for Small Molecules
Two new floes are introduced in this release to build graph convolutional neural network (GCNN) models and to use those models for predictions. GCNNs are desirable models primarily because they can learn directly from the molecular graph using atom and bond features from OpenEye toolkits rather than features derived from the molecule (e.g., fingerprints), resulting in fewer parameters for the model to learn. GCNNs are also not limited to interaction radii from complex structures, therefore building more generalizable models.
The new floes are ML Build: Graph Convolution Model on Pregenerated Features for Small Molecules and ML Predict: Graph Convolution Model Prediction. To support these new floes, the ML Build and Predict: Optimal Property-Predicting Graph Convolutional Neural Network Model tutorial and the How to Build and Predict Optimal Property-Predicting Graph Convolutional Neural Network Machine Learning Models by Tweaking Neural Network Architecture how-to-guide have been added to the documentation.
Output analysis in these floes now includes information about how the number of parameters in the model compares to the amount of data. Warnings are included if overfitting based on this ratio is a concern.
Cryptic Pocket Detection Floes
v0.3.2 September 2025
General Notice
This package is built using
OpenEye-toolkits==2025.1.1,OpenEye-orionplatform==6.7.0,OpenEye-Snowball==0.30.0, andOpenEye-orionmdcore==2.5.4.
Minor Changes
Floes now assign missing atomic radii directly to make them more robust to a variety of protein preparation methods.
The Automated Cryptic Pocket Detection with Probe Occupancy Analysis, Combined Probe Binding Site Analysis, Probe Occupancy Analysis, Dynamic Probe Binding Analysis, and Exposon Analysis Floes have been improved to use the normalized ligandability score in their pocket filtration.
The Automated Cryptic Pocket Detection with Probe Occupancy Analysis, Combined Probe Binding Site Analysis, Probe Occupancy Analysis, Dynamic Probe Binding Analysis, and Exposon Analysis Floes now correctly output multiple holo design units superposed with the pocket receptors.
The Run a Normal Mode-Guided Weighted Ensemble MD Simulation Floe was previously titled the Run a Weighted Ensemble MD Simulation Floe. Similarly, the Continue a Normal Mode-Guided Weighted Ensemble MD Simulation Floe was previously titled the Continue a Weighted Ensemble MD Simulation Floe. These changes have been made to specify that these floes use protein normal modes as progress coordinates for driving the weighted ensemble simulations.
Format Conversion (ETL) Floes
v6.7.0 September 2025
General Notice
This package is built using
OpenEye-orionplatform==6.7.0andOpenEye-toolkits==2025.1.1.
Functional Changes
There is a new floe for archiving files and datasets.
Machine Learning Model Building Floes
v1.0.2 September 2025
This package is built using
OpenEye-orionplatform==6.7.0,OpenEye-toolkits==2025.1.1,OpenEye-Snowball==0.29.2, andOpenEye-floereport==6.7.0.
Feature Updates
New floes have been added to allow for model building and property prediction using Graph Convolutional Neural Network (GCNN) models. GCNNs can learn directly from the molecular graph using atom and bond features from OpenEye toolkits rather than features derived from the molecule (e.g., fingerprints), resulting in fewer parameters for the model to learn. GCNNs are also not limited to interaction radii from complex structures, therefore building more generalizable models.
A new parameter, Graph Feature Vector Generation, has been added to the Data Processing of Small Molecule for ML Model Building Floe. This parameter builds graph feature tensors and outputs a collection with graph nodes and edge features that will be used as input for the GCNN model building floe.
There is an informative new chapter on How to Build Optimal Property-Predicting Graph Convolutional Neural Network Machine Learning Models by Tweaking Neural Network Architecture.
New Floes
These floes have been introduced and described in the new ML Build and Predict: Optimal Property-Predicting Graph Convolutional Neural Network Model tutorial:
Molecular Dynamics Affinity
v 6.5.7 September 2025
General Notice
This version pins
orionmdcore==2.5.3.1, where temporary resources are deleted immediately after use.The NES chimera construction has been improved to avoid cube failures during ring fusion involving a cyclopropyl group.
Molecular Dynamics Core Package
v2.5.5 September 2025
General Notice
This package is built using
openeye-orionplatform >=5.1.1, <7,openeye-snowball >=0.26.0,openeye-toolkits >=2023.2.3,openff-toolkit >=0.14.4, <0.15, andparmed ==3.4.4.
Updates
Legacy cubes and API points have been removed to upgrade old data formats.
Temporary resources are now deleted immediately after use.
Bug Fixes
A bug has been fixed that could cause Gromacs to crash when multiple water residue names were present.
pKa Prediction Floes
v0.2.0 September 2025
General Notice
This package is built using
OpenEye-toolkits==2025.1.1,OpenEye-orionplatform==6.7.0, andOpenEye-Snowball==0.30.0.
Feature Updates
The resonance has been fixed in cases where unfavorable structures were generated due to enumerating protonated and deprotonated states of atoms within or around aromatic rings.
The LogD calculation has been improved.
The UI/UX experience in workfloe Job Forms has been improved.
Structural Biology Floes
v0.1.2 September 2025
General Notice
This package is built using
OpenEye-toolkits==2025.1.1,OpenEye-orionplatform==6.7.0,OpenEye-Snowball==0.30.0, andOpenEye-orionmdcore==2.5.4.This is the first release of the OpenEye Structural Biology Floes package.