OEFPAtomType
This namespace contains atom typing options that can be used when generating Circular, Path of Tree fingerprints. Atom type options control how the atoms of the enumerated circular, path or tree fragments are encoded during the fingerprint generation.
The OEFPAtomType namespace contains the following constants:
Constant name |
Combination of |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note
The constants of the OEFPAtomType
namespace can be combined using the bitwise OR
operation.
Note
The images in this sections visualize the effect of the various atom typing options.
See also
Visualizing Molecule Similarity section
See also
OEFPBondTypenamespaceOEMakeCircularFPfunctionOEMakePathFPfunctionOEMakeTreeFPfunctionAtom and Bond Typing section
Note
All explicit hydrogens are suppressed of the molecule before generating any fingerprints. (See example in Example of molecules that are considered to be equivalent due to suppressing their explicit hydrogens).
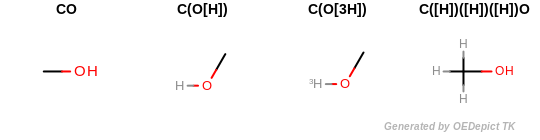
Example of molecules that are considered to be equivalent due to suppressing their explicit hydrogens
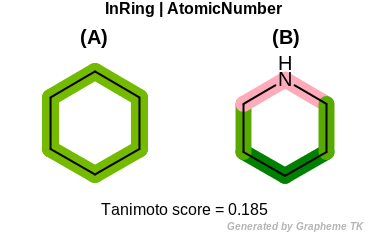
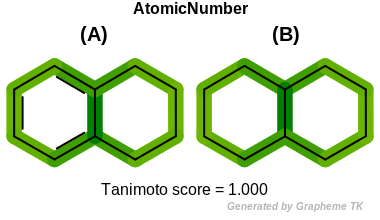
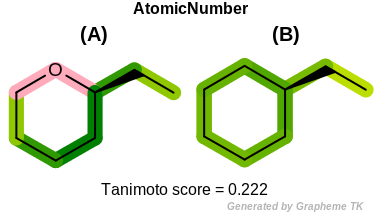
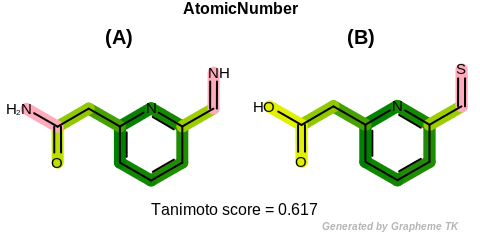
AtomicNumber
This flag indicates that atomic number (the value returned
by the OEAtomBase::GetAtomicNum method) is encoded
into the generated fingerprint, i.e., if two fragments (either
circular, paths or tree) are composed of atoms with different
atomic numbers, then the two fragments will be mapped to different
bits of the fingerprint.
Table: Example of using the AtomicNumber option
demonstrates the effect of using the OEFPAtomType::AtomicNumber flag.
|
|
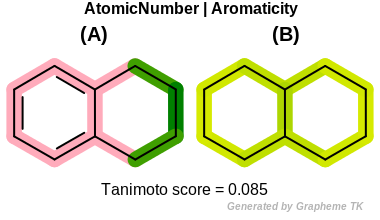
Aromaticity
This flag indicates that aromaticity (the value returned by the
OEAtomBase::IsAromatic method) is
encoded into the generated fingerprint, i.e., an aromatic
and an aliphatic fragment will be mapped to different bits of the
fingerprint.
Table: Example of using the Aromatic option
demonstrates the effect of using the OEFPAtomType::Aromaticity flag.
|
|
Note
Prior to generating a fingerprint, the aromaticity of the
molecule is re-perceived using the OEAroModel::OpenEye
aromaticity model.
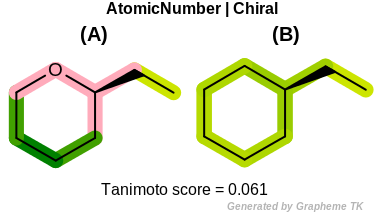
Chiral
This flag indicates that chiral and non-chiral atoms (the value
returned by the OEAtomBase::IsChiral method) are
distinguished during the fingerprint generation.
Table: Example of using the Chiral option
demonstrates the effect of using the OEFPAtomType::Chiral flag.
|
|
Note
Different stereoisomers of molecules can not be distinguished
when the OEFPAtomType::Chiral flag is set.
(See example in Figure: Example of molecule similarity of stereoisomers).
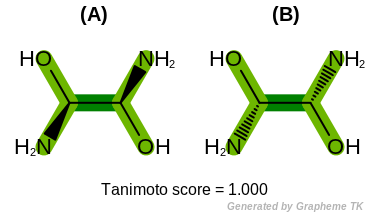
Example of molecule similarity of stereoisomers
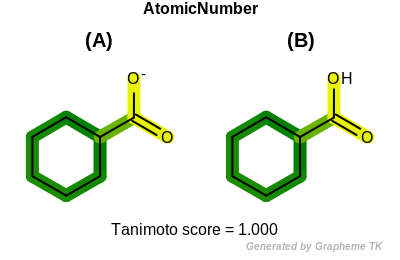
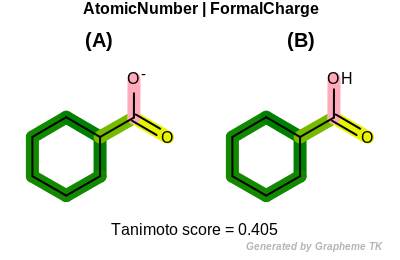
FormalCharge
This flag indicates that formal charge (the value returned by the
OEAtomBase::GetFormalCharge method) is encoded into the
generated fingerprint.
Table: Example of using the FormalCharge option
demonstrates the effect of using the OEFPAtomType::FormalCharge flag.
|
|
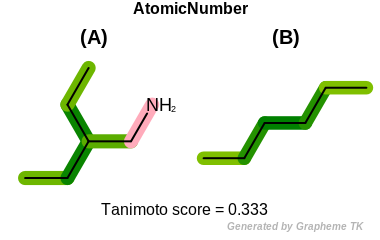
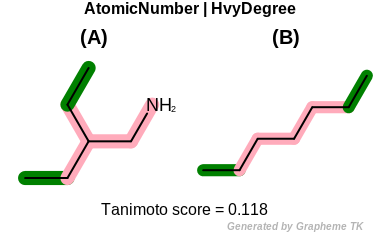
HvyDegree
This flag indicates that heavy degree information (the value
returned by the OEAtomBase::GetHvyDegree
method) is encoded into the generated fingerprint.
Table: Example of using the HvyDegree option
demonstrates the effect of using the OEFPAtomType::HvyDegree flag.
|
|
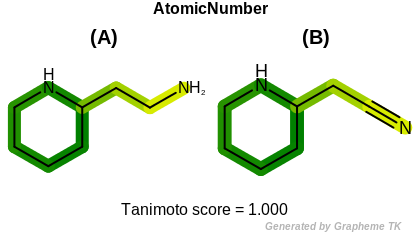
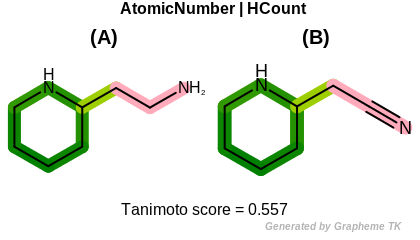
HCount
This flag indicates that number of hydrogens (the value
returned by the OEAtomBase::GetTotalHCount method)
is encoded into the generated fingerprint.
Table: Example of using the HCount option
demonstrates the effect of using the OEFPAtomType::HCount flag.
|
|
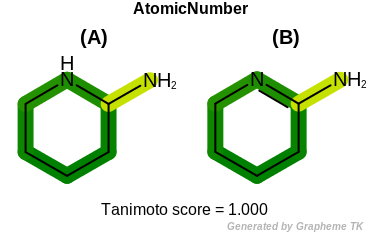
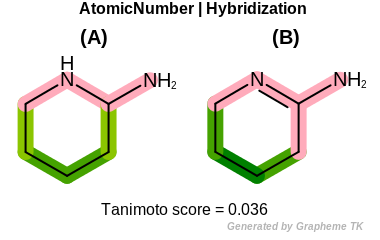
Hybridization
This flag indicates that hybridization (the value returned by the
OEAtomBase::GetHyb method) is encoded into the
generated fingerprint.
Table: Example of using the Hybridization option
demonstrates the effect of using the OEFPAtomType::Hybridization flag.
|
|
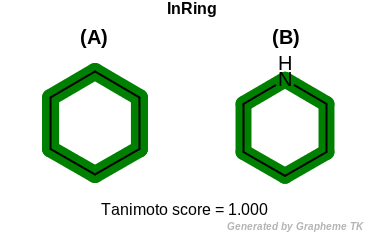
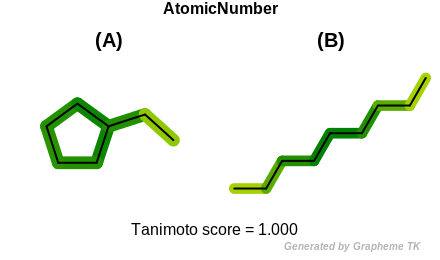
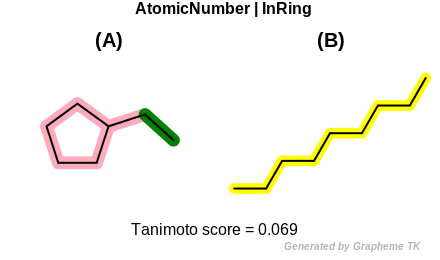
InRing
This flag indicates that atom topology (the value returned by the
OEAtomBase::IsInRing method) is encoded into the generated fingerprint,
i.e., if two fragments (either circular, path or tree) are composed of atoms
with different atom topology, then the two fragments will be mapped to
different bits of the fingerprint.
Table: Example of using the InRing option
demonstrates the effect of using the OEFPAtomType::InRing flag.
|
|
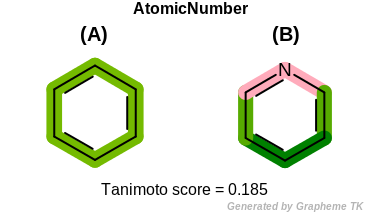
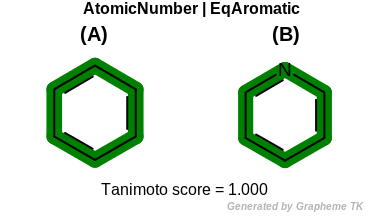
EqAromatic
This flag modifies the meaning of the
OEFPAtomType::AtomicNumber flag.
If the OEFPAtomType::EqAromatic flag is
set then aromatic atoms are considered equivalent during the fingerprint
generation.
Table: Example of using the EqAromatic option
demonstrates the effect of using the OEFPAtomType::EqAromatic flag.
|
|
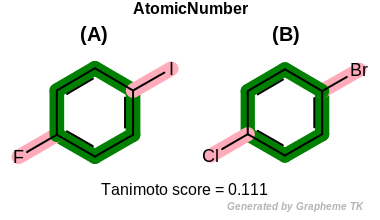
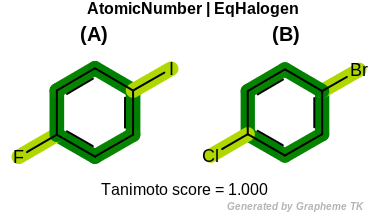
EqHalogen
This flag modifies the meaning of
OEFPAtomType::AtomicNumber flag.
If the OEFPAtomType::EqHalogen flag is
set then halide atoms (OEElemNo::F,
OEElemNo::Cl, OEElemNo::Br, and
OEElemNo::I) are considered equivalent during
the fingerprint generation.
Table: Example of using the EqHalogen option
demonstrates the effect of using the OEFPAtomType::EqHalogen flag.
|
|
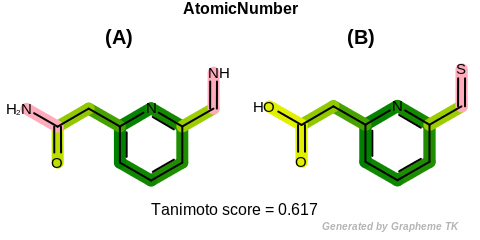
EqHBondAcceptor
This flag modifies the meaning of the
OEFPAtomType::AtomicNumber flag.
If the OEFPAtomType::EqHBondAcceptor flag
is set then atoms that are perceived as hydrogen bonding
acceptors are considered equivalent during the fingerprint
generation.
The GraphSim TK uses the same definition as the MolProp TK
to identify hydrogen bond acceptors.
See examples in Figure: Molecules with hydrogen bond acceptor annotation.
Table: Example of using the EqHBondAcceptor option
demonstrates the effect of using the OEFPAtomType::EqHBondAcceptor flag.
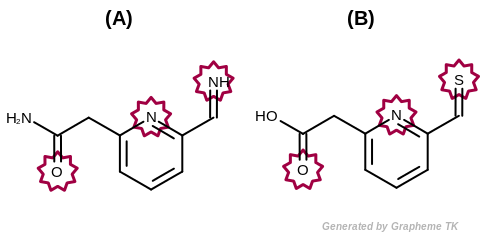
Example of molecules with hydrogen bond acceptor annotation
|
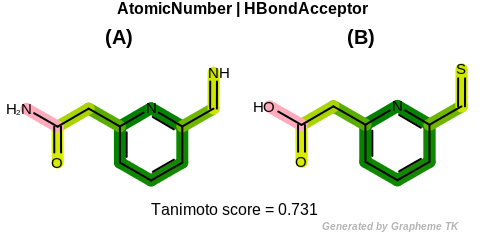
|
EqHBondDonor
This flag modifies the meaning of the
OEFPAtomType::AtomicNumber flag.
If the OEFPAtomType::EqHBondDonor flag is
set then atoms that are perceived as hydrogen bonding donors
are considered equivalent during the fingerprint generation.
The GraphSim TK uses the same definition as the MolProp TK
to identify hydrogen bond donors.
See examples in Figure: Molecules with hydrogen bond donor annotation.
Table: Example of using the EqHBondDonor option
demonstrates the effect of using the OEFPAtomType::EqHBondDonor flag.
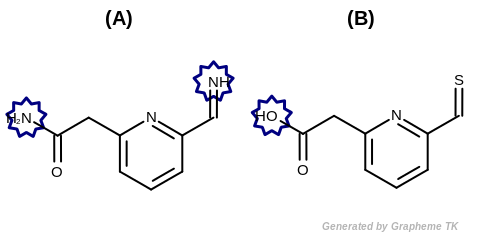
Molecules with hydrogen bond donor annotation
|
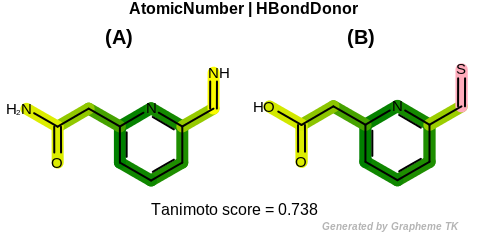
|
DefaultAtom
Same as DefaultPathAtom constant.
DefaultCircularAtom
The bitwise OR’d value of the following atom typing options:
See example in Figure: Circular fingerprint similarity with default circular atom and bond typing.
This constant is used as atom typing parameter when a default
Circular fingerprint is
generated by the following functions:
OEMakeFP(OEFingerPrint &, const OEMolBase &,OEFPType::Circular)OEMakeCircularFP(OEFingerPrint &, const OEMolBase &)
See also
OEFPBondType::DefaultCircularBondconstant
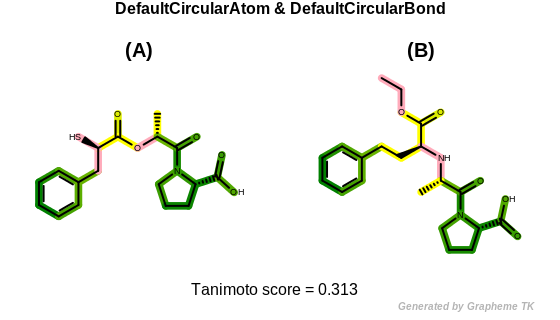
Circular fingerprint similarity with default circular atom and bond typing
DefaultCircularVSAtom
The default atom typing for the circular fingerprint that is designed for virtual
screening. It is the same as DefaultCircularAtom
without OEFPAtomType::FormalCharge.
DefaultPathAtom
The bitwise OR’d value of the following atom typing options:
See example in Figure: Path fingerprint similarity with default path atom and bond typing.
This constant is used as atom typing parameter when a default
Path fingerprint is
generated by the following functions:
OEMakeFP(OEFingerPrint &, const OEMolBase &,OEFPType::Path)OEMakePathFP(OEFingerPrint &, const OEMolBase &)
See also
OEFPBondType::DefaultPathBondconstant
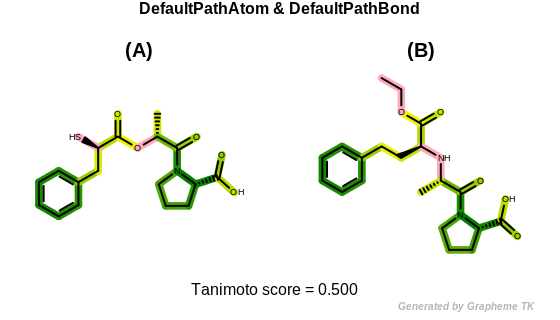
Path fingerprint similarity with default path atom and bond typing
DefaultPathVSAtom
The default atom typing for the path fingerprint that is designed for virtual
screening. It is the same as DefaultPathAtom
without OEFPAtomType::FormalCharge and
OEFPAtomType::Hybridization.
DefaultTreeAtom
The bitwise OR’d value of the following atom typing options:
See example in Figure: Tree fingerprint similarity with default tree atom and bond typing.
This constant is used as atom typing parameter when a default
Tree fingerprint is
generated by the following functions:
OEMakeFP(OEFingerPrint &, const OEMolBase &,OEFPType::Tree)OEMakeTreeFP(OEFingerPrint &, const OEMolBase &)
See also
OEFPBondType::DefaultTreeBondconstant
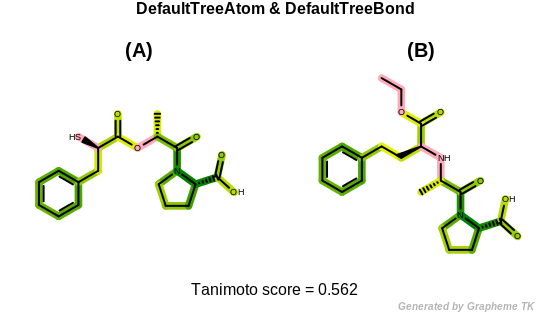
Tree fingerprint similarity with default tree atom and bond typing
DefaultTreeVSAtom
The default atom typing for the tree fingerprint that is designed for virtual
screening. It is the same as DefaultTreeAtom
without OEFPAtomType::FormalCharge and
OEFPAtomType::Hybridization.
None
No atom properties are encoded when generating a fingerprint.